The 5 Types of Followers in Leadership has been taken into the context of a popular and charismatic leader and a dominating voice. Nevertheless, the efficiency of any leader depends greatly on their followers. Followers do not remain as silent spectators in the process of management; they shape the way it heads, the impression it creates, and the effectiveness it achieves. As a matter of fact, leadership is an interactive process, and followers are equally important as the leaders.
Perhaps the most commonly accepted model that discusses this idea is the model of followership issued by Robert E. Kelley. His study moved the attention away from leaders to followers and pointed out the role of the followers and their actions towards organizational success.
The 5 types of followers identified in the model by Kelley include alienated, conformist, pragmatist, passive, and effective followers, and we shall expound on them in this blog. Each of the types of leaders also contributes differently to the leadership process, which involves different levels of critical thinking and participation.
The title of the group 5 Types of Followers is a reference to Kelley categorizing styles of following followers according to the degree of their independence in thought and participation. The awareness of these groups can assist leaders to build stronger teams and empower people in an attempt to become more productive members.
What are the 5 Followers Types?
Robert E. Kelley was a revolutionary in the direction of new thought pursued in leadership when he published his article in the Harvard Business Review in 1992, which highlighted the element of followers. The model refers to Kelley, who points out differences in individuals in terms of critical thinking and active endeavours, two factors that characterize behaviours of followers. With the consideration of these characteristics, Kelley identified five different types of followers, or in totality, the 5 types of followers.
So here is a short description of each:
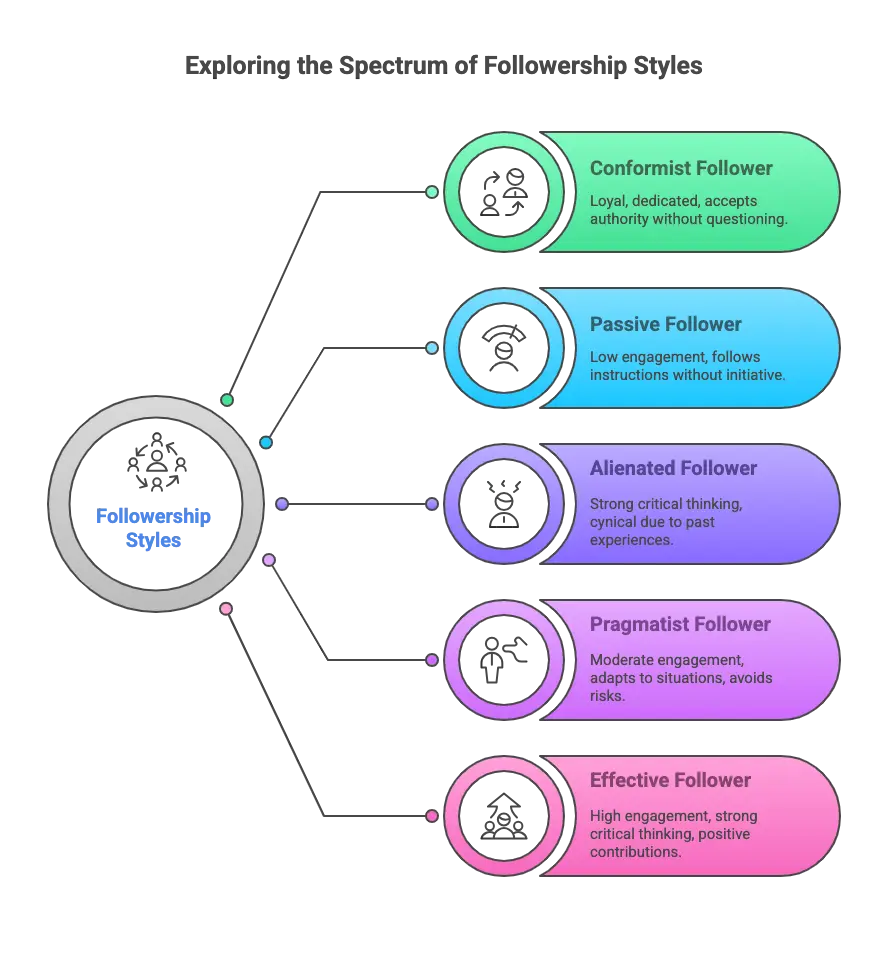
- Conformist Follower: These are very active individuals who have a low level of critical thinking about their activities. They are loyal and stick to it, although they readily accept authority blindly.
- Passive Follower- Passive followers are low-way and low-engagement critical thinkers. They tend to do whatever they are told to do, and their contribution remains little.
- Alienated Follower followers are strong in terms of critical thinking, as well as low in engagement. They are usually cynical or unbelieving, and their unbelieving nature may be a result of having bad experiences in leadership.
- Pragmatist Follower – They work in the intermediate space and are medium both in engagement and critical thinking. They adjust to circumstances and never take adventurous stands.
- Effective Follower: Such a follower is the best possible type of follower, and he is an extremely engaging and critical thinker. They make positive contributions, contribute to healthy constructive challenge, and help leaders to become effective leaders.
Knowing the 5 categories of followers assists organizations in discovering advantages, overcoming deficiencies, and creating groups that achieve positively under various types of leadership styles.
Type 1: conformist follower
Definition and Main characteristics: A conformist adherent works extremely diligently on behalf of a leader and cannot think on his/her own. They are eager to follow instructions and diligently perform tasks without really questioning the authority or considering the option of alternatives. Conformists are loyal, steady, and positive, the people who are usually regarded as the yes men who want to be liked.
- An illustration of this at the workplace is: Take the case of a junior marketing associate who never contradicts the strategy of the manager, although he/she may hold some reservations about it. They perform unpaid work, ensure they meet their deadlines, and do not argue with people, yet they do not come up with creative ideas or oppose unrealistic plans.
A list of pros and cons: Pros:
- Good staff with good backgrounds.
- Stable and trustworthy, it makes it easy to run the task.
- Well-disposed to the objectives of leadership.
Cons:
- Innovation or critique deficiency
- Giving loyalty to ill-founded decisions riskily
- Have the ability to strengthen non-productive leadership practices
Strategies of Leadership for dealing with conformists: To control conformist followers, the following strategies should be followed:
- Ask them to give their opinions to encourage their approach towards thinking independently.
- Establish an environment of criticism and criticism in place of dissent
- Offer decision-making and leadership experiences
- Indicates that there is good disagreement
When their critical thinking skills are cultivated and developed, the followers will become better workers for the organization and transform into effective change agents.
Type 2: Follow-me Follower
The meaning of Passive Follower in Management. A passive follower is a person who still has very low levels of independent thinking and active involvement. Passive followers in management language tend to wait to be told what to do, are not keen on responsibility, and can only deliver more than the bare requirements. They do not question people or propose any solutions, and are highly dependent on the leadership to give them directions.

Behavioral Characteristics and the Possible Dangers: Passive followers normally:
- Avert venture
- Do not talk when conversing
- Will require checking at all times
- show no interest or emotional commitment
Such characteristics are dangerous to organizational performance. Passive followership teams might not perform well in the area of innovation, problems might not be solved on time, and it might pressurize the managers, who will now have to keep a check and guide.
Real-World Scenario:
At that, you cannot imagine an administrative assistant just performing his job only when he is told to do so. They do not project demands and will not voice complaints when they make a mistake. When faced with a task that is not in their job description, they await the suggestions of a manager to take action, even in an emergency. Inability to take initiative can destroy the work process and decision-making.
The Way Leaders Can Turn the Engagement On: These steps that a leader can take to make passive followers more active members of a team are the following:
- Establish high standards that focus on the aspect of proactivity and ownership
- Provide mentoring and skill-building to gain confidence
- Just pay attention to little actions to stimulate gradual development
- To be able to feel initiative, delegate duties that allow some autonomy
Knowing how to reach passive followers and establish a space of psychological security and responsibility, leaders are able to engage more deeply on their side and slowly transform passivity into positive, useful interaction.
Type: 3: Alienated FollowerGood Follower vs Alienated Follower:
The alienated as well as effective followers have good critical thinking skills. Nevertheless, unlike effective followers, alienated followers are unreceptive towards leaders and are usually not prone to authority. They can raise questions, but normally destructively or sarcastically, as they can be disappointed or disillusioned about what has happened in the past.
What Causes Alienation in Organizations: Alienation usually arises out of:
- Ineffective leadership (e.g., Micromanagement, lack of ethics)
- Recognition or trust deficiency
- Repeated occurrences of ignoring or dismissing ideas
- Injustice or miscommunication between organisations
With time, high-potential people will retreat and become more critical and distanced, thereby becoming alienated followers.
The Reason This Type is Important to Leadership: The followers who feel alienated might portray themselves to be unengaged; nevertheless, they might possess useful knowledge and abilities. Failure to consider their point of view may lead to growth and innovation opportunities. In addition, their dissatisfaction can affect other people, which may begin to transfer the negative energy to the team.
The following are tips on how to re-engage the alienated followers:
- Restore confidence through openness to admit the errors of the past and show stability
- Encourage them to offer their contribution during strategic talks, and demonstrate that their opinion counts
- Give them some useful work to restore an idea of usefulness and usefulness
- Get peers to collaborate with them to reintroduce them into the team dynamic
With the proper help, alienated followers can become renamed as effective followers, the kind that question authority in healthy, progressive fashions.
Type 4:Pragmatist FollowerDefinition and Characteristic features:
The middle point on the scale of Kelley is represented by a follower who is a pragmatist, demonstrating average amounts of independent thought and involvement. Such people are prudent, versatile, and politically savvy. They do not openly defy authority, but at the same time, they are not submissive. Pragmatists are like a fish that follows the flow and remains nonchalant until it is safe or beneficial to do otherwise.
Flexibility to Leadership Patterns: Pragmatist adherents are adaptive and modify their performance to the approach of a leader and the organizational culture. They can be more active, more careful through a participative environment. With dictatorial leadership, they might swing back to the self-preservation mode, going to extremes of doing what has to be done but without jeopardizing themselves by making trouble.
The Strengths and Challenges: Strengths:
- Confident and believing in a crisis
- Do not fall on either end of the spectrum between blind loyalty and the obvious cynicism
- Works well in environments that are highly complex/political
Challenges:
- Risk-averse; do not like to speak up or take initiatives
- Can be opposed to innovation or change, especially when seen as dangerous
- stand to maintain the status quo out of fear of reprisal
Management Advice in Practice: To efficiently lead the pragmatist followers:
- Discuss the matter openly so that you can gradually empower their minds.
- Set them up to have low-stakes situations where they can lead or speak out
- Write what evaluates reflective thinking
- Integrity and transparency of models in a bid to diminish the political prudence she has to compromise
Given the proper conditions, pragmatists will also be efficient group players who do not undermine the group dynamics.
Type 5: The reason why Good Followers Are Leaders in Disguise:
Good followers live up to the ideal of the model described by Kelley as they are proactive, free thinkers, and are heavily involved. Such people do not require instructions and they are ready to accept responsibilities, speak out their minds, and uphold organizational objectives through honesty. To a great extent, efficient followers are leaders who have no authority.
Qualities That Would Be Helpful To Them:

- Excellent level of critical thinking
- Independent management and responsibilities
- Positive criticism and input
- Simple identification with the team and organizational objectives
Passive, Active Mid-grade Differences: Effective followers live on responsibility and critical thinking, which are avoided by the passive followers. The bare-bones followers only do the minimum expected, and effective followers go out of their way to question, contribute, and cooperate to improve results.
Promoting Better Followers in Your Team: The ways through which leaders can produce effective followers are by:
- Energizing decision-making at the bottom-up phases
- Honor privilege and self-reliance
- Creating an atmosphere of trust and honesty
- The provision of growth possibilities through mentorship and feedback
Through the development of followership, organizations are able to have a rather competent but also quite aligned with organizational leadership in terms of vision and performance.
Why Follower Types Matter in Leadership?
The Problem of Follower Types in Leadership is highly important because teams need to be productive and well-balanced, and this requires recognition of the 5 types of followers. Both kinds, starting with passive and ending with effective, come along with different behaviours that affect the area of communication, innovation, and overall team performance. Although good followers act as a catalyst to excellent performance and advancement, bad followers might hinder a move or behave against change.
Transformational leadership is one of the leadership theories that teaches the importance of the two-way interaction between the followers and the leaders. On the same note, practitioners in the real world acknowledge that morale, retention, and success are little influenced by follower behavior. To illustrate the point, it is often the case that tech startups flourish with competent and pragmatist disciples who can be both productive and realistic in their innovations. Bureaucratic organizational settings, on the other hand, can be a source of passive or conformist cultures accidentally.
Learning the type of followers will help a leader to change their tactics, mentor alienated followers, wake up the sleepers, and give power to productive members. Such knowledge transforms leadership into a commanding top-to-bottom approach to the development of an energetic partnership involving feedback, growth, and alignment in both directions.
Essentially, the concept of identifying the importance of followership should not only be used as a strategy to win the hearts of subordinates; instead, it should be seen as a strategic insignia to organizational success on whichever platform.
How to Manage Different Kinds of Followers
Ways to Deal with Types of FollowersLeadership is not confined to giving directions and requires knowledge of how followers differ in their behaviors and how to deal with them. All 5 types of followers described by Kelley in his model demand specific approaches to leadership in the process of creating engagement, accountability, and growth.
| Conformist Followers: They grow well in organisation and direction but tend to stifle creativity. Strategy: Promote a free flow of ideas and encourage creativity. Communication Tip: Request them to share their views during a meeting to encourage them to be involved. Leadership Style: supportive and participative, and promoting psychological safety. |
| Passive Followers: These people are waiting to be told what to do, and they do not take initiative. Strategy: Create Behavioral goals, offer systematic mentoring, and reward mini-victories. Communicating Tip: Employ action-oriented, positive words, and achieve that ownership stress. Leadership Style- Coaching and developmental with an orientation to gain confidence and autonomy. |
| Passive Followers: Such people are waiting to be told what to do and are not taking action. Strategy: Establish specific expectations, Skillful mentoring, and breakthroughs on small accomplishments. Communication Tip: An encouraging language that directly uses ownership language should be used. Style of Leadership: Coaching and developmental, which is concerned with developing confidence and independence |
| Alienated Followers: Those who have lost interest because they have felt bad previously.Plan: Restore trust, listen to what they are saying, and give them important roles.Communication Tip: Be open and realize their contributions.Leadership Style: Transformational, to renew meaning and belonging. |
| Pragmatist Followers: They are risk-averse, but balanced and with a status quo. Strategy: Put them through mini-leadership roles and experiences of experimentation with a degree of safety. Communication Tip: Encourage constructive risk-taking by insisting on their worth.Leadership Style: Democratic, structured, and autonomous. |
| Effective Followers: Active, autonomous, and perfect team players.Strategy: Put into the hands of strategic responsibilities, empower them, and make them part of the process of decision-making. Communication Tip: Appreciate them and request that they be mentors to other people. Leadership Style: Delegative/ collaborative and viewing them as partners in leadership. |
When cutting performance to the maximum, development of the potential, and the formation of resilient, adaptive teams, managers should focus on aligning leadership styles with the behavior of followers.
Conclusion
The 5 classifications of the followers, namely: conformist, passive, alienated, pragmatist, and effective, bring to attention that leadership is not a practice that fits all. Managing to identify and address the various behavioral styles of followers can result in a business model change and improved performance of teams.
Follower-awareness is not only a possession of a leader, but it is a key to engagement, innovation, and trust. By recognizing the type of each individual team member, you will be in a position to influence your team members to cooperate harmoniously with one another.
This is the right time to assess your group relationships and management approach. Do you bring up productive followers? Do you contribute to developing others into nonconformist or nonpassive persons? The leadership process starts with listening, and better leadership starts by understanding the followers.




